Rapid Prototyping: The Key to Successful Product Development
The most important findings at a glance
Rapid prototyping as a bridge: Transferring CAD designs into physical models to validate design, functionality, and manufacturability before series production – an indispensable component of every product development process.
Proven manufacturing processes: 3D printing enables rapid iterations of complex geometries, CNC machining delivers precise metal and plastic prototypes, and injection molding produces near-series parts – the right technology for every requirement.
Concrete advantages for companies: Minimized risk through early testing, cost savings compared to late-stage production changes, accelerated time to market through parallel development processes, and informed decisions based on real-world insights.
Cross-Industry Significance: From automotive to medical technology to aerospace – prototype construction is the key to market readiness and competitiveness in all industries with complex products.
MakerVerse as Partner: Instant quote after CAD upload, broad technology portfolio (3D printing, CNC, injection molding), verified supply chain, engineering support – everything from single prototypes to small series from a single source.
Start Your Manufacturing Project with MakerVerse
MakerVerse is a platform for sourcing industrial parts. It provides instant access to a vetted supply chain and a full range of manufacturing technologies. With AI-powered quoting, order management, and fulfilment, MakerVerse helps with everything from initial prototypes to full-scale production.
What is Rapid Prototyping?
Rapid prototyping refers to the production of early product models to validate design, functionality and manufacturability before series production. A prototype is a physical model that makes the idea tangible – unlike the final product, it primarily serves for testing and optimization. Through prototyping, designers can test designs, make changes and minimize risks before costly tools for production are created.

Rapid prototyping is an iterative process. From the initial idea through several optimization loops to the production-ready design, prototypes go through various development phases. Three types are fundamentally distinguished:
- Concept Prototypes: Early models for checking basic feasibility and visualizing the product idea – often still without complete functionality.
- Functional Prototypes: Prototypes with complete or partial function for testing under real conditions – focus is on validation of technical requirements and user interaction.
- Pre-Series Prototypes: Production-like prototypes with final materials and manufacturing processes for validation of the entire production process before market launch.
Why is Rapid Prototyping Important for Product Development?
Prototype manufacturing is an indispensable component of modern product development and offers companies measurable advantages. Physical models allow risks to be identified early and costs to be significantly reduced – fixing errors in the prototyping phase is demonstrably much cheaper than corrections in series production.
- Early Error Detection: Design errors, material problems or manufacturing obstacles are identified before mass production. This prevents expensive corrections to tools and significantly reduces scrap rates in series production.
- Validation of Functionality and Design: Prototypes enable realistic testing under operating conditions. Engineers test mechanical resilience, fit accuracy and user-friendliness before production starts.
- Feedback Integration: Physical models facilitate communication between engineers, designers and customers. Stakeholders can touch, test and contribute concrete improvement suggestions – far more effective than CAD representations alone.
- Risk Minimization: Tests under real conditions reveal weaknesses that were overlooked in digital design. This applies especially to complex assemblies with multiple components.
- Accelerated Market Launch: Through iterative development and parallel testing, time to market readiness is shortened. Rapid prototyping enables multiple optimization cycles in weeks instead of months.
- Improved Collaboration: Tangible prototypes create a common basis for interdisciplinary teams and considerably facilitate decisions on design changes.
Tip: Platforms like MakerVerse additionally shorten the procurement process – instead of days of quote communication with various suppliers, you receive a binding quote within minutes.
Which Rapid Prototyping Methods Exist?
Four manufacturing methods have become established in industrial prototype production and cover different requirements – from quick concept models to series-like pre-production parts. The choice of the right method depends on factors such as material requirements, geometric complexity, quantity and budget.
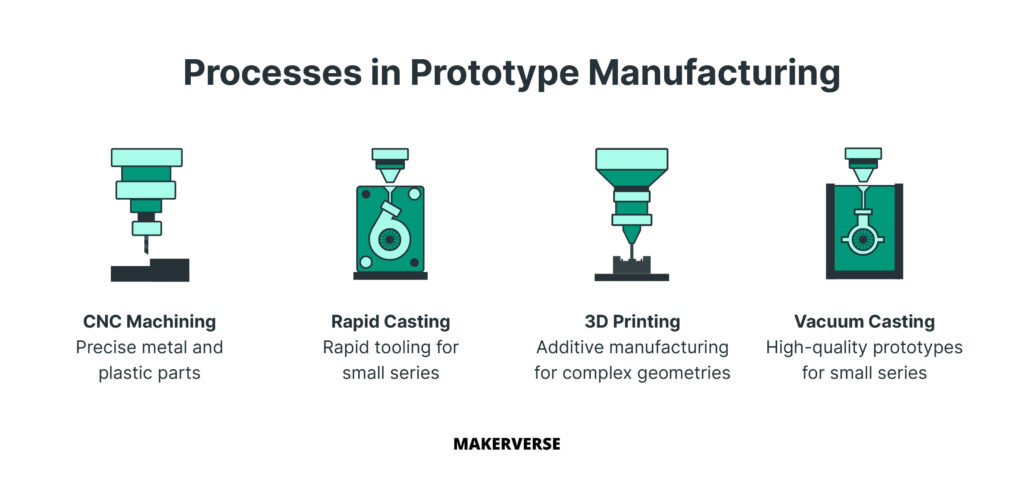
3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
3D printing has established itself as the leading rapid prototyping method through its layer-by-layer material buildup. Based on CAD data, complex geometries are created without tooling costs – a decisive advantage over traditional manufacturing methods. Production often takes place within a few days, which significantly accelerates iterative development processes.
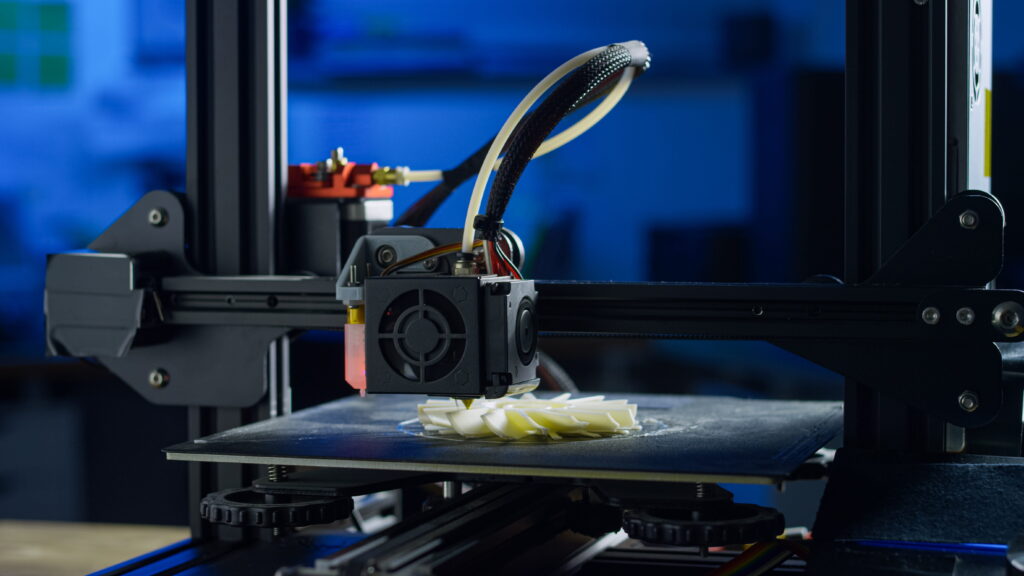

The most important additive methods include SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) for robust plastic parts, SLA (Stereolithography) for high-precision models with smooth surfaces, FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) as a cost-effective entry-level technology and MJF (Multi Jet Fusion) for production-like prototypes. The material variety ranges from technical plastics to resins to metals – depending on requirements for strength, temperature resistance or surface quality.
Typical applications include functional prototypes for validation of mechanical properties, design models for presentations and small series from 1 to 100 pieces. Especially with complex geometries that would be difficult to realize with CNC machining, additive manufacturing demonstrates its strengths and enables designers maximum design freedom without compromises.
At MakerVerse, all common additive methods are available – from SLS to SLA to MJF. The verified supply chain ensures that your prototypes reliably meet the specified requirements.
CNC Machining for Metal and Plastic Prototypes
CNC machining (Computer Numerical Control) is a subtractive manufacturing method in which material is precisely removed from a blank. The main processes include CNC milling for complex contours and pockets as well as CNC turning for rotationally symmetrical parts. This method offers high precision and dimensional accuracy, excellent surface quality and a wide material selection – from metals like aluminum, steel and titanium to technical plastics like ABS and PEEK.
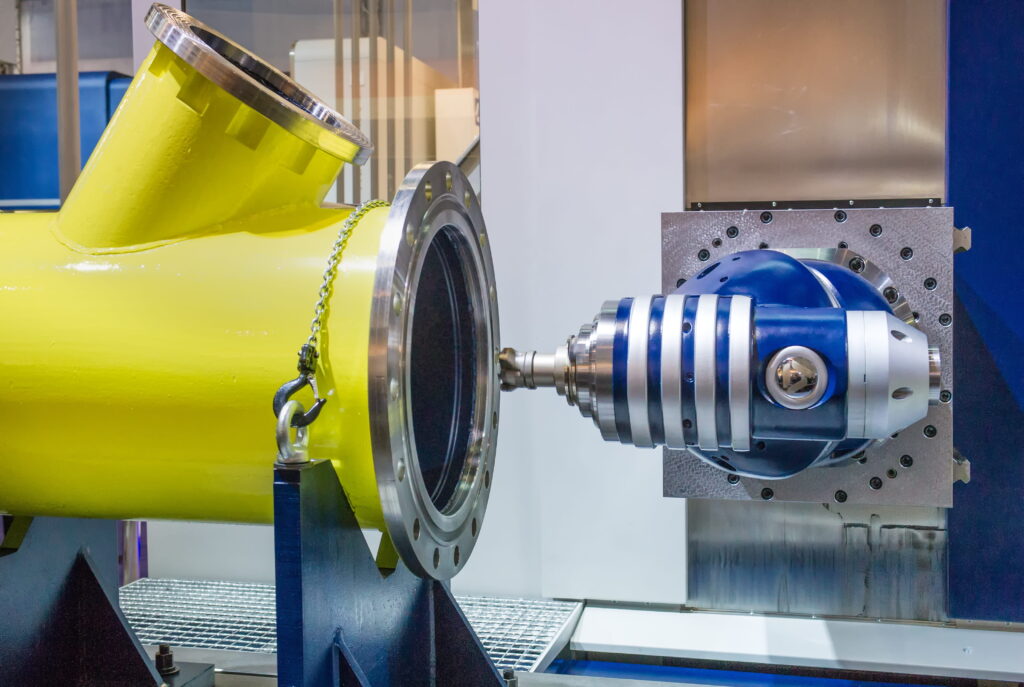
CNC machining is ideally suited for functional prototypes that must withstand mechanical loads, prototypes with tight tolerances and pre-series parts that should be close to later production. An important aspect from practice: Design optimization significantly reduces costs. Radii instead of sharp edges avoid additional machining steps, and the ratio of pocket depth to width directly influences tool selection. Small, deep pockets require fragile cutters and longer machining times – conscious design therefore noticeably reduces manufacturing effort and thus costs.
Injection Molding and Rapid Tooling
In injection molding for prototypes, liquid plastic is injected into a mold under high pressure – the method corresponds to that of series production. The crucial difference: Rapid tooling uses quickly manufactured aluminum molds instead of expensive steel tools. These molds can be manufactured in a few weeks and enable the production of series-like prototypes with the same materials as the final product. The method is suitable for quantities from 50 to over 10,000 parts and allows realistic testing of the later production process.

The economic advantages are significant: Tooling costs are well below those for series tools, while part quality delivers production-like results. This makes injection molding ideal for design validation before investing in expensive series tools. Companies can conduct market tests with production-like parts and obtain customer feedback before committing to final tools. Typical applications include housing parts for electronics, consumer goods with high volumes and technical components where material properties and surface quality must match series production. The transition from prototype to series production is seamless through switching to steel tools while maintaining the same processes.
Vacuum Casting for Small Series and Series-Like Prototypes
Vacuum casting closes the gap between 3D printing and injection molding. The method uses silicone molds that are molded from a 3D-printed or CNC-manufactured master model. Under vacuum, polyurethane resin is poured into the mold – the result are parts with injection-molding-like properties, but without the high tooling costs.
The strengths of vacuum casting lie in small series of 10 to 50 pieces, when 3D printing becomes too expensive but injection molding tools are not yet worthwhile. Typical applications include housing parts for market tests, functional prototypes with series-like haptics and pre-series for customer presentations. Part quality is suitable for realistic product testing – surfaces, colors and mechanical properties can be reproduced close to the final product.
Start Your Manufacturing Project with MakerVerse
MakerVerse is a platform for sourcing industrial parts. It provides instant access to a vetted supply chain and a full range of manufacturing technologies. With AI-powered quoting, order management, and fulfilment, MakerVerse helps with everything from initial prototypes to full-scale production.
The Prototyping Process: From Idea to Finished Prototype
Prototyping is not a linear but an iterative process – multiple prototype generations are normal and each iteration improves the product step by step. From the initial idea to market readiness, prototypes typically go through the following phases:
- Concept Development and Initial Designs: The idea is concretized, requirements for functionality, design and manufacturability are defined. Designers create initial sketches and establish technical framework conditions.
- CAD Design and Technical Construction: Engineers create a detailed 3D model with all relevant dimensions, tolerances and material specifications. This digital design forms the basis for all following steps.
- Selection of Manufacturing Methods and Materials: Based on requirements, budget and timeframe, designers select the optimal method (3D printing, CNC machining, injection molding) and suitable materials.
- Prototype Manufacturing: The physical model is produced – depending on method and complexity, this takes from a few hours to several weeks.
- Testing and Validation: The prototype is tested for functionality, fit accuracy and resilience. Insights from these tests flow directly into optimization.
- Feedback Integration and Optimization: Changes are made based on test results and feedback from engineers, customers or users. The design is refined.
- Iteration to Market Readiness: Steps 2 to 6 are run through multiple times until the final product meets all requirements and is production-ready. Each cycle brings the product closer to series production.
Practice Tip: The MakerVerse material advisor supports optimal material selection based on mechanical requirements, temperature resistance and budget.

Rapid Prototyping at MakerVerse: How It Works
MakerVerse offers a digital platform that simplifies the entire prototyping process – from the initial idea to delivery of quality-tested prototypes. The service combines state-of-the-art manufacturing technologies with transparent processes and personal consultation from experienced engineers.
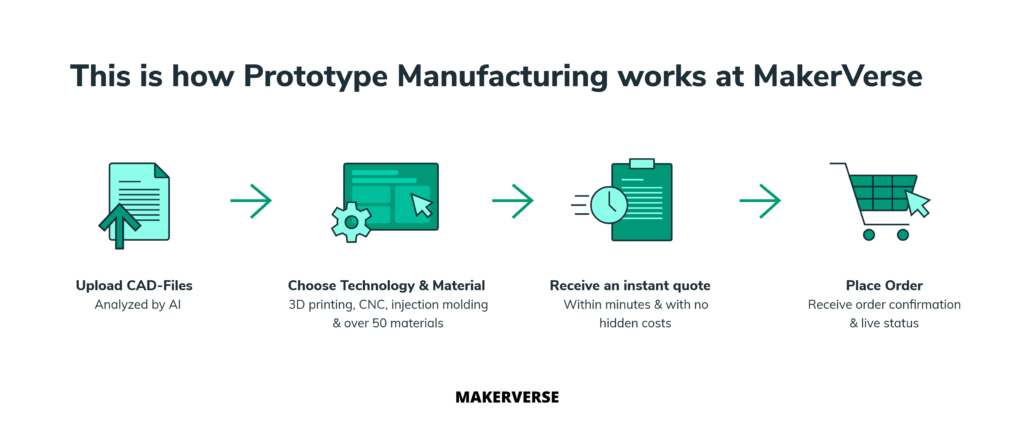
The process is designed to be simple. Upload your CAD file in common formats such as STEP or STL. Then select the appropriate technology (3D printing, CNC machining or injection molding) as well as the desired material. Within a very short time, you receive an automatic quote with transparent prices and binding delivery time. After your order, quality-tested manufacturing takes place through verified partners from our network, before the finished parts are delivered directly to you.
The advantages of MakerVerse for your prototype manufacturing:
- Broad Technology Portfolio: Access to all important manufacturing methods under one roof – from 3D printing to CNC to injection molding.
- Instant Quote Without Waiting Time: No time-consuming email communication with various suppliers – transparent calculation in minutes instead of days.
- Verified Supply Chain: All partners undergo strict quality controls so that your prototypes reliably meet requirements.
- Engineering Support When Needed: Personal contact for complex projects, technical meetings for design optimization and consultation on selecting the optimal method.
- Flexible Quantities: From single prototypes for initial tests to small series for market tests – MakerVerse accompanies you in every phase of product development.
Start now: Upload your CAD file and receive your instant quote for professional rapid prototyping within minutes.
Start Your Manufacturing Project with MakerVerse
MakerVerse is a platform for sourcing industrial parts. It provides instant access to a vetted supply chain and a full range of manufacturing technologies. With AI-powered quoting, order management, and fulfilment, MakerVerse helps with everything from initial prototypes to full-scale production.
FAQ
How much does a prototype cost?
Costs vary greatly depending on manufacturing method, material, size and complexity of the component. Simple 3D printed parts start at a few euros, while complex CNC parts made of metal or injection molding tools can cost several thousand euros. MakerVerse offers an instant quote after CAD upload – so you receive transparent calculation without waiting time and can directly compare costs with different methods and materials.
What does a prototype builder do?
A prototype builder transforms CAD designs into physical prototypes and selects suitable manufacturing methods based on technical requirements. Consultation on design optimization (Design for Manufacturing) is part of it, as well as quality control and iterative adjustments during development. The work combines technical know-how with practical manufacturing experience – engineers and designers work closely together to develop a production-ready component from the idea.
In which industries is rapid prototyping used?
Prototyping finds cross-industry application: Automotive uses it for vehicle components and test parts, medical technology for medical devices and implants, aerospace for lightweight components under extreme requirements. Consumer goods, electronics, mechanical engineering and robotics also rely on prototype construction. Practically every industry with product development uses prototypes for validation before market launch – from the first idea to series production.
What advantages does rapid prototyping offer compared to traditional methods?
With rapid prototyping, development times are drastically shortened – prototypes are created in days instead of weeks. Costs decrease through the elimination of expensive tools, while design freedom increases. Faster iteration cycles enable more tests and optimizations in less time. Companies can conduct market tests earlier and obtain customer feedback, which accelerates market launch and minimizes the risk of misdevelopments.